前言
闲来无事,还是决定重新拾起C,开个新坑充当笔记本+碎碎念。至于rust,要不明天开始?
使用教材
多大教授所写APS105 Computer Fundamentals的电子书
也附上Github仓库地址:Github Repository
Chapter 1: Basic structure of computers and Binary systems
计算机中的数据存储方式
在学习C语言之前,对计算机存储数据原理的了解是非常重要的。在现代计算机中,一般使用二进制来存储数据
举个例子:
| 十进制 | 二进制 |
|---|---|
| 0 | 00 |
| 1 | 01 |
| 2 | 10 |
| 3 | 11 |
两位数二进制数字可以存储0-3,以此类推三位数便可存储0-7。
不难发现,n位数字可以表示 $0 \sim (2^n - 1)$ ,同理要表示n个数字,我们需要 $ \log_2(x) $
在现代计算机中,一个字节(byte)由 8 位(bit)组成。千字节(KB)等于 1024 字节。兆字节(MB)等于 1024 千字节。吉字节(GB)等于 1024 兆字节。太字节(TB)等于 1024 吉字节。
数据寻址
所有数据都需要地址,数据两部分,现代计算机使用64-bits来表示地址,一共可以表示 $ 2^64 $个不同的地址,每个地址对应一个字节的数据。也就是说64-bits寻址可以存储16 Exabyte的数据
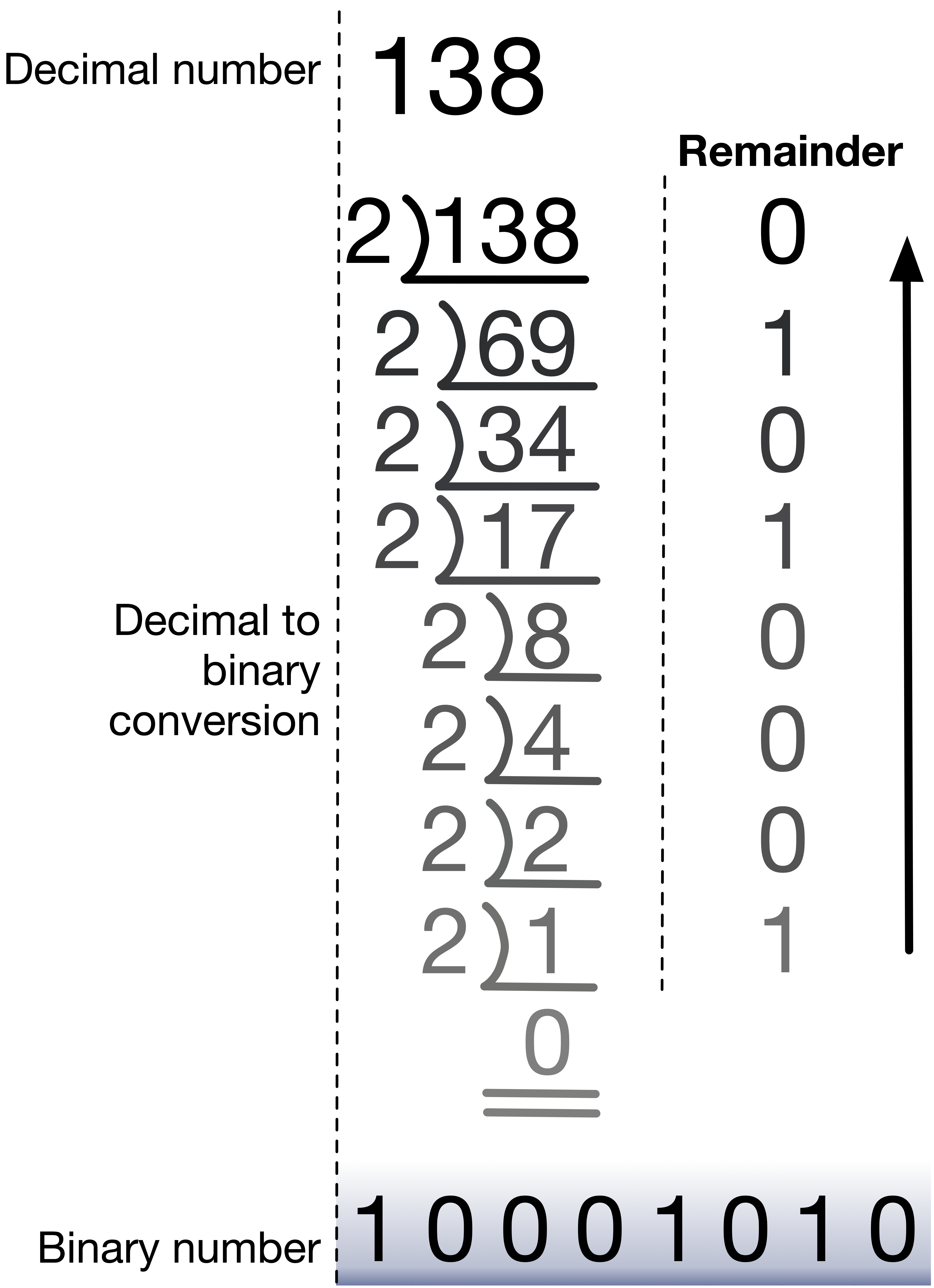
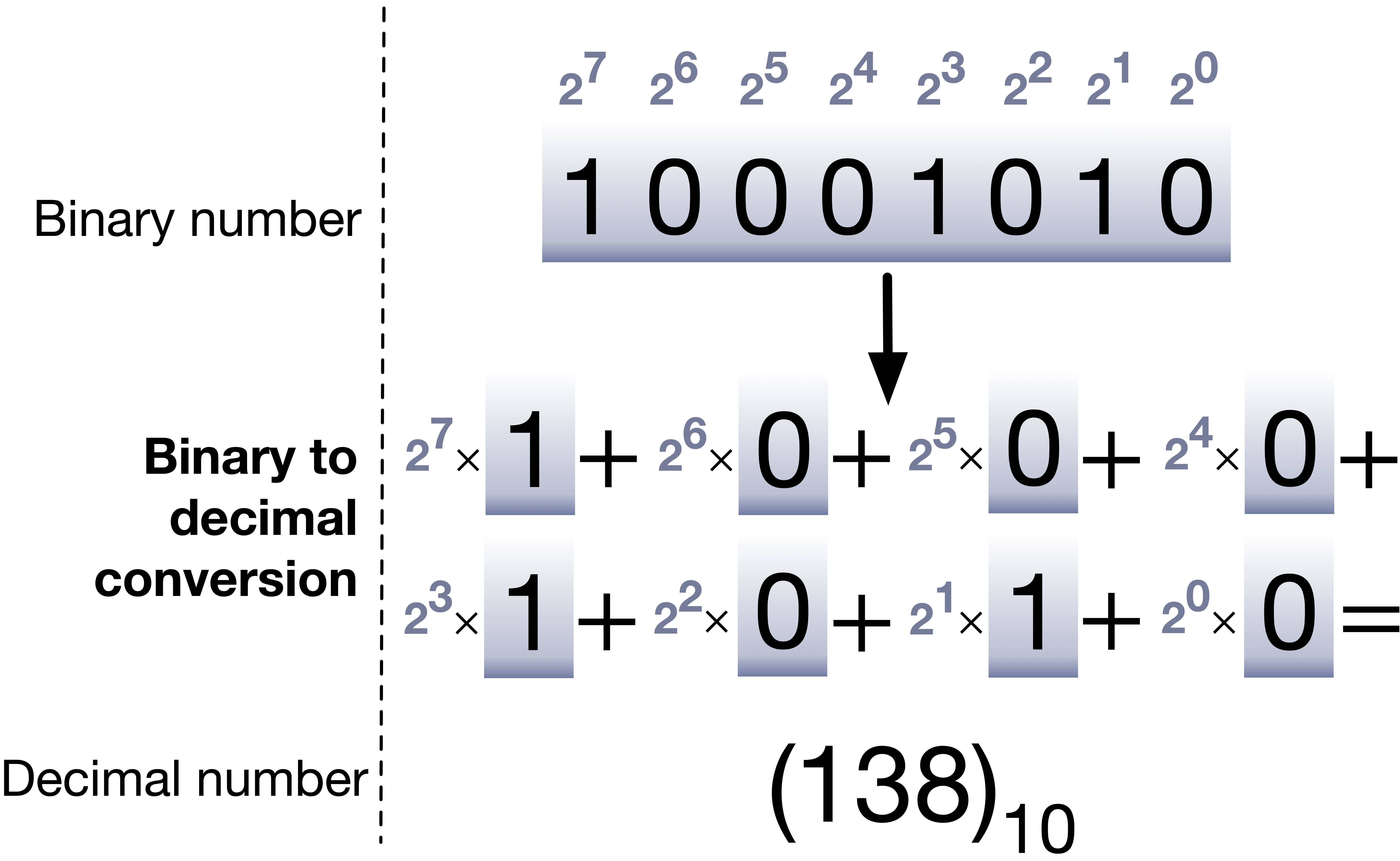
进制转换
这一部分偏数学,且较容易理解,故放两张图
Chapter 2 Data operation and representation
2.2 数据类型与表示
基础数据类型
| 类型 | Format Specifier | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
int |
%d |
整数,正或负,4-bytes (32bit) |
unsigned int |
无符号整数,4-bytes, 0 ~ 2^32 - 1$ | |
float |
%f |
单精度浮点数,4-bytes |
double |
%lf |
双精度浮点数, 8-bytes |
char |
%c |
字符, 1-bytes, 使用ASCII码存储 |
bool |
%d |
布尔值, 1-bytes |
Boolean
不同于C++, 在C中使用boolean需要导入库:
1 |
变量初始化
不同与Python等语言,在C/C++中变量在使用前需要显式的声明
如果一个变量没有赋初始值,变量的初始值不是0!相反,初始值会是内存中该位置的值(可以理解为随机值)
使用scanf读取值
1 |
|
注意,scanf传入的是变量的地址而非变量 (e.g. &integer, &是地址运算符)
2.3 Operations
运算结果是什么类型?
在C中算数运算的结果始终是精度更高的被运算数的类型, 更高精度的数据类型有传染性
举个例子:
1 | int x = 10*5/3; |
上述代码的运算结果会是int 类型,运算结果的小数部分会被无情截断
终极玄学之 ++i与i++
++i是前缀,即递增发生在语句中。因此,j = ++i;等价于j = i = i + 1;。由于赋值运算符的存在,计算是从右到左进行的。而
i++是后缀,即对i的递增发生在语句之后。这意味着j = i++;等价于j = i; i = i + 1;。
可以尝试
1 |
|
类型转换 Type casting
1 | double x = (double) 3/2 |
sizeof()运算符
用于获取在当前操作系统中用于存储某个数据类型所需的字节数(amount of byte)
2.4 数学库 Math Library
| 数学符号表示法 | 函数原型 | 它有什么作用? | 示例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| $x$ | double sqrt(double x); |
返回 x 的平方根 |
sqrt(4) 返回 2.0 |
| $x^y$ | double pow(double x, double y); |
返回 x 的 y 次方 |
pow(2, 3) 返回 8.0 |
| $e^x$ | double exp(double x); |
返回 e (欧拉数)的 x 次方 |
exp(1) 返回 2.718281828459045 |
| $\log(x)$ | double log10(double x); |
返回 x 的以 10 为底的对数 |
log10(100) 返回 2.0 |
| $\ln(x)$ | double log(double x); |
返回 x 的自然对数 |
log(M_E) 2 返回 1.0 |
| $\left |x \right|$ | double fabs(double x); |
返回 x 的绝对值 |
fabs(-2) 返回 2.0 |
| $\sin(x)$ | double sin(double x); |
返回 x 的正弦值,其中 x 以弧度(而非角度)为单位 |
sin(M_PI * 2) 3 返回 0.0 |
| $\cos(x)$ | double cos(double x); |
返回 x 的余弦值,其中 x 以弧度(而非角度)为单位 |
cos(M_PI * 2) 3 返回 1.0 |
| $\tan(x)$ | double tan(double x); |
返回 x 的正切值,其中 x 以弧度(而非角度)为单位 |
tan(M_PI) 3 返回 0.0 |
| $\sin^−1(x)$ 或 $\arcsin(x)$ | double asin(double x); |
返回 x 的反正弦值(以弧度为单位,而非角度) |
asin(0.5) 返回 0.523599 |
| $\cos^−1(x)$ 或 $\arccos(x)$ | double acos(double x); |
返回 x 的反余弦值(以弧度为单位,而非角度) |
acos(0.5) 返回 1.047198 |
| $\tan^−1(x)$ 或 $\arctan(x)$ | double atan(double x); |
返回以弧度(而非角度)表示的 x 的反正切值 |
atan(2) 返回 1.107149 |
| max(x) | double fmax(double x, double y); |
返回 x 和 y 中的最大值 |
fmax(3.2, -7.9) 返回 3.2 |
| min(x) | double fmin(double x, double y); |
返回 x 和 y 中的最小值 |
fmin(-6.1, -7.3) 返回 -7.3 |
| ⌊x⌋ | double floor(double x); |
返回小于或等于 x 的最大整数,即对 x 向下取整 |
floor(9.6) 返回 9.0 |
| ⌈x⌉ | double ceil(double x); |
返回大于或等于 x 的最小整数,即对 x 向上取整 |
ceil(3.09) 返回 4.0 |
x % y |
double fmod(double x, double y); |
返回 x / y 的余数 4。请记住, % 运算符仅适用于 int 操作数,而 fmod 也适用于 double 操作数。 |
fmod(5.3, 2.1) 返回 1.1 |
| ⌊x⌉ | double rint(double x); |
返回最接近 x 的整数,即对 x 进行四舍五入 |
rint(-2.1) 返回 -2.0 |
About this Post
This post is written by Jinyuan Zhou, licensed under CC BY-NC 4.0.